What the $#&^!@* is Direct Assessment of Student Social and Emotional Learning Skill?
I think you’ll agree with me that terminology is, well… boring. But let’s also admit that not understanding terminology can cause problems, like, for example, leading you to choose the wrong SEL student skill assessment.
In recent conversations with educators and others about SEL assessment, I’ve learned that the meaning of “direct assessment” is often not clear. Because of that, the value of direct assessment is also often not clear. I’m on a mission to fix that.
Here’s the quick definition: Direct SEL skill assessments are measures that require students to solve challenging social and emotional problems and thereby demonstrate their social and emotional skills. The rest of this blog explains what this means, with examples, and how to direct assessment differs from other methods.
Illustrating Direct Social and Emotional Assessment and Contrasting it with Other Methods
Let’s imagine for a moment that:
- you want to assess a specific student social and emotional skills,
- you decide, based on research, standards, and SEL program content to assess social awareness,
- you decide that as part of that, you want to assess children’s ability to read social cues about others’ emotions.
You’ll be faced immediately with the question of how to assess this skill. Here are the most commonly available methods, and an example to illustrate how they work:
- With self-report, children rate their own skill level, often by indicating how true of them a series of statements are (or how frequently they engage in various behaviors). In this case, a self-report item might look like this:

- With teacher reports, teachers rate student skill level, typically by rating the frequency of student behaviors. In this case, a teacher report item might look like this:
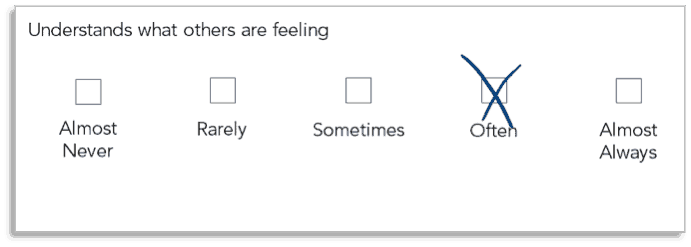
- With direct assessment, children demonstrate their skills by solving social and emotional problems. In this case, a direct assessment item might ask a child to determine what a person is feeling from their facial expression, like this:

See the difference? With direct assessment, students demonstrate their skill by applying that skill to a social and emotional problem. In this case, the problem is figuring out what someone is feeling.
Other methods of assessment are possible too, such as observation, direct behavior ratings, and peer nominations. But self-report, teacher report, and direct assessments are the most commonly used, so let’s stick with those three for now.
In summary, with self-report, students tell you about their skills; with teacher reports, teachers tell you about student skills; with direct assessment, students demonstrate their skills. In an earlier blog post, I described these as “show” assessments (direct) and “tell” assessments (self-report and teacher report).
Direct Assessment’s Sweet Spot
Understanding the term matters because direct assessment does some things particularly well. For one, direct assessment is well-suited to assessing social-emotional skills that involve thinking and, some aspects of self-regulation. Thinking processes are invisible, so it can be hard for teachers to know how well-developed these skills are; students may also be unable or unwilling to report their skill level. But direct assessments give a better window into these thinking skills children bring to social interactions.
For example, SELweb, our direct assessment of SEL skill, assesses four skills that are well-suited to direct assessment: emotion recognition, social perspective-taking, social problem-solving, and self-control.
We chose to assess those skills because research shows that they are associated with a host of important outcomes. In addition, they are reflected in widely cited models of SEL, such as the CASEL model:
| This SELweb skill… | Is part of this CASEL competence… |
| Emotion recognition | Social Awareness |
| Social perspective-taking | Social Awareness |
| Social problem-solving | Responsible Decision-Making |
| Self-Control | Self-Management |
We also chose to assess these skills because they are included in existing and emerging state guidelines and standards, and the skills SELweb measures are represented in widely-used SEL programs:
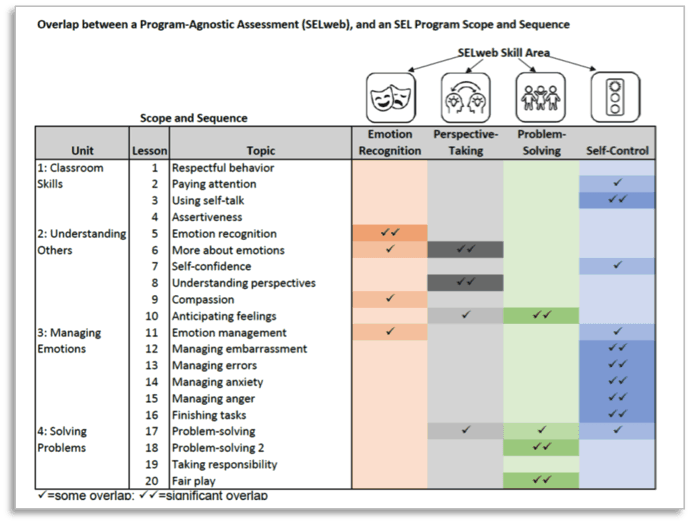
When should you consider direct assessment? When the skills you want to assess are hard to observe or when you want to assess children’s ability to demonstrate those skills by applying them to social and emotional problems.



